
Flexor and Extensor digitorum longus muscles Google Search Muscle
Extending from the wrist to the elbow joint is the region of the upper extremity called the forearm (antebrachium). The forearm helps the shoulder and the arm in force application and the precise placement of the hand in space, with the help of the elbow and radioulnar joints.. This article is a guide to help you master the anatomy of the forearm and the elbow joint, using the beautiful.

Difference Between Flexor and Extensor Muscles Compare the Difference
The extensor tendon over the hand, wrist, and distal forearm is amenable to core sutures, similar to flexor tendon repairs, whereas the extensor tendon distal to the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint is often surprisingly thin.. (E) Passive flexion following extensor tenolysis and PIP dorsal capsulotomy. (A-C,.

Explain the Difference Between a Flexor and Extensor Muscle
The extensor tendon compartments of the wrist are six tunnels which transmit the long extensor tendons from the forearm into the hand. They are located on the posterior aspect of the wrist. Each tunnel is lined internally by a synovial sheath and separated from one another by fibrous septa.. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the extensor compartments of the wrist - their.
Notes on Anatomy and Physiology One Big Tendon
Skeletal muscles are found on the bone, interact with bones for movement and are voluntarily controlled. When performing a workout, we activate the body's skeletal muscle groups to create movement and burn calories. Flexors and extensors are at the core of this. Together, they bend and straighten the body's joints to create motion and activate.

Wrist Flexors Muscles Wrist Flexor Tendon Anatomy Anatomy Human Body
There are many ways to repair a cut tendon, and certain types of cuts need a specific type of surgical tendon repair. Our hand surgeons at Emory will discuss the best treatment option for your specific flexor tendon injury. If you have questions, or to make an appointment, call: 404-778-3350.
Hand Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
Extensor muscles help in straightening or extending whereas flexor muscles help in bending our elbows, knees and fingers. Flexor and extensor muscles initiate flexion and extension in our body respectively. Read this article to find out a detailed explanation of the muscles and also important differences between them.
FLEXOR AND EXTENSOR TENDONS OF THE HAND pediagenosis
Extensor tendinitis can be caused by anything that makes you use your hands or feet in a repetitive motion. Over time, the normal wear and strain builds up on your extensor tendons and causes irritation. That irritation makes your tendons swell (become inflamed). That inflammation is what causes pain and makes it hard for your tendons to move.

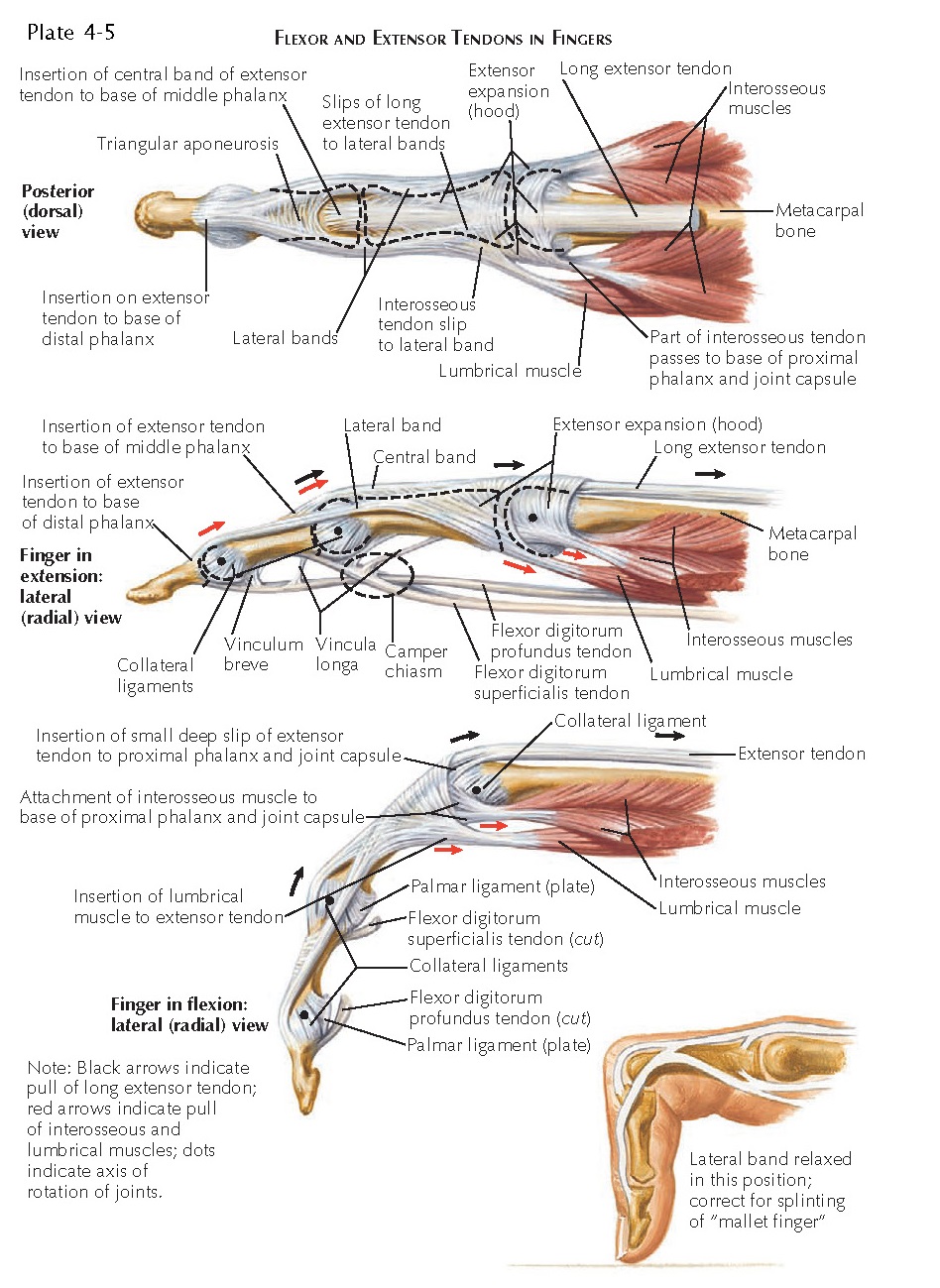
Flexor and Extensor Tendons in the Finger TrialExhibits Inc.
The forearm is the section of the upper limb from the elbow to the wrist, whose bony structure is formed by the radius (laterally) and ulna (medially). Two muscular compartments - an anterior (flexor) and posterior (extensor) compartment - contain together twenty muscles that act on the elbow and wrist joints, as well as carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal, and interphalangeal joints of the hand.

Anatomy lesson forearm wrist musculature Artofit
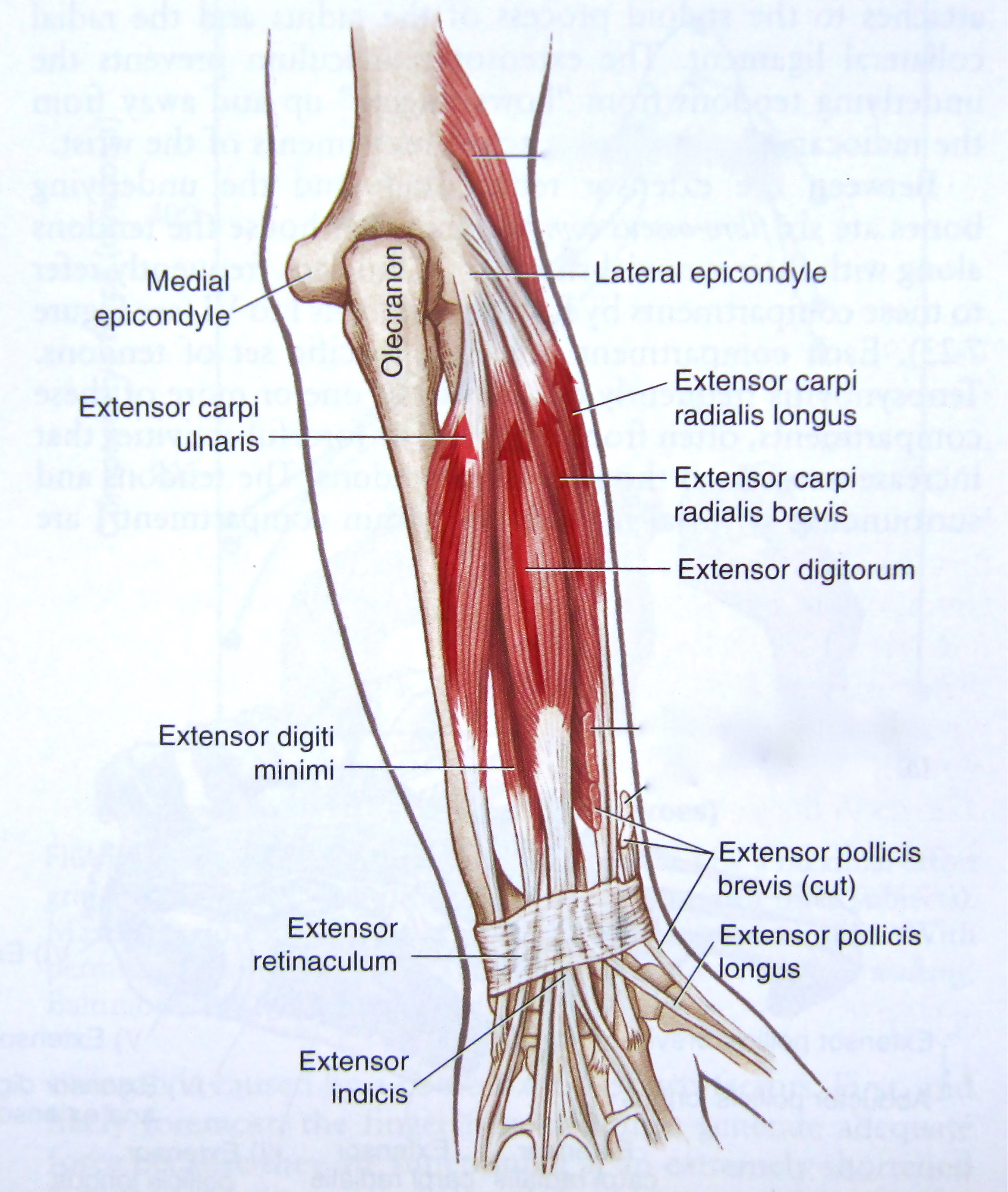
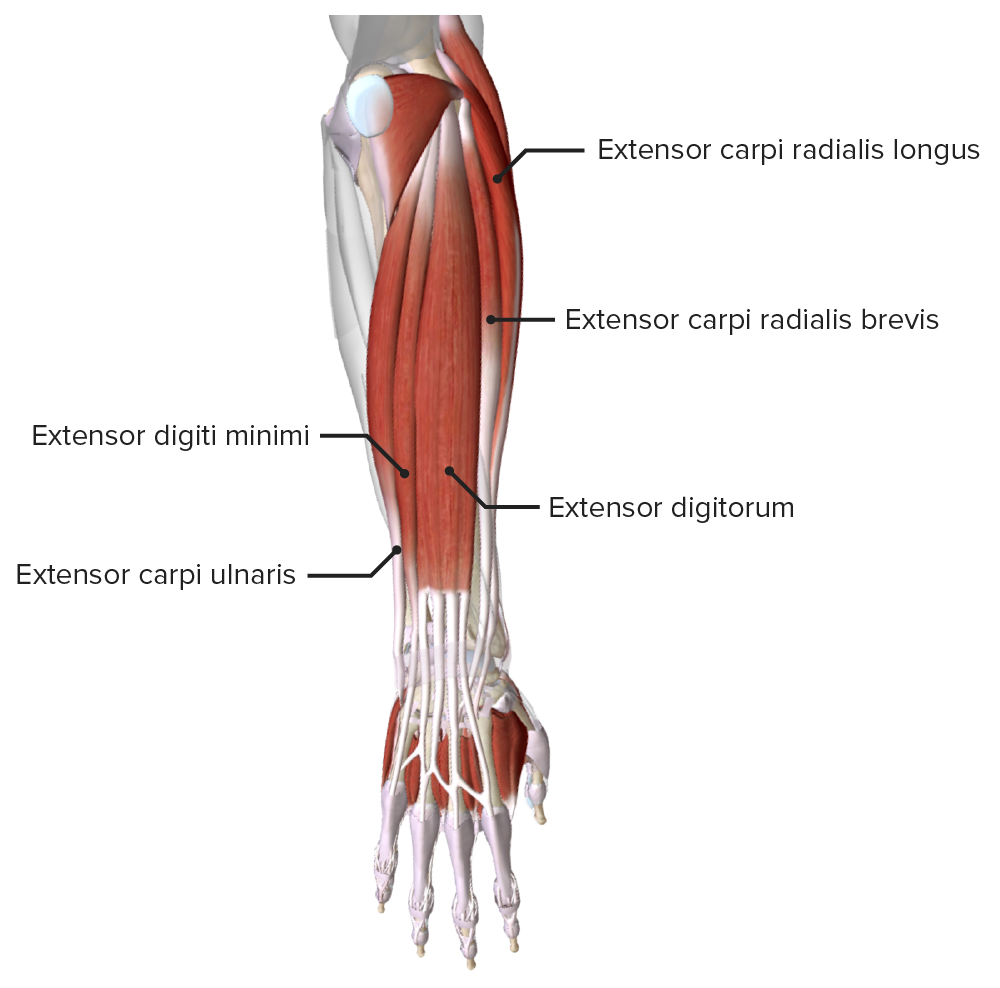
The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle is an elongated fusiform muscle located in the posterior compartment of the forearm and primarily functions to extend and adduct the wrist. It spans between the elbow and the base of the little finger. The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle belongs to the superficial group of extensors of the forearm along with brachioradialis, anconeus, extensor carpi radialis.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12820/forearm-extensor-muscles_english.jpg)
Learn forearm extensor muscle anatomy with quizzes Kenhub
Maximal isokinetic strength ratios of joint flexors and extensors are important parameters to indicate the level of muscular balance at the joint. Further, in combat sports athletes, upper and lower limb muscle strength is affected by the type of sport. Thus, this study aimed to examine the differences in maximal isokinetic strength of the flexors and extensors and the corresponding flexor.

Wrist Flexors Muscles Snphysio Flexors And Extensors Of The Forearm
Extensor muscles are responsible for extending or straightening a joint, while flexor muscles are responsible for flexing or bending a joint. Extensor muscles are typically located on the posterior side of the body, such as the triceps in the upper arm or the quadriceps in the thigh. On the other hand, flexor muscles are usually found on the.
Hand Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
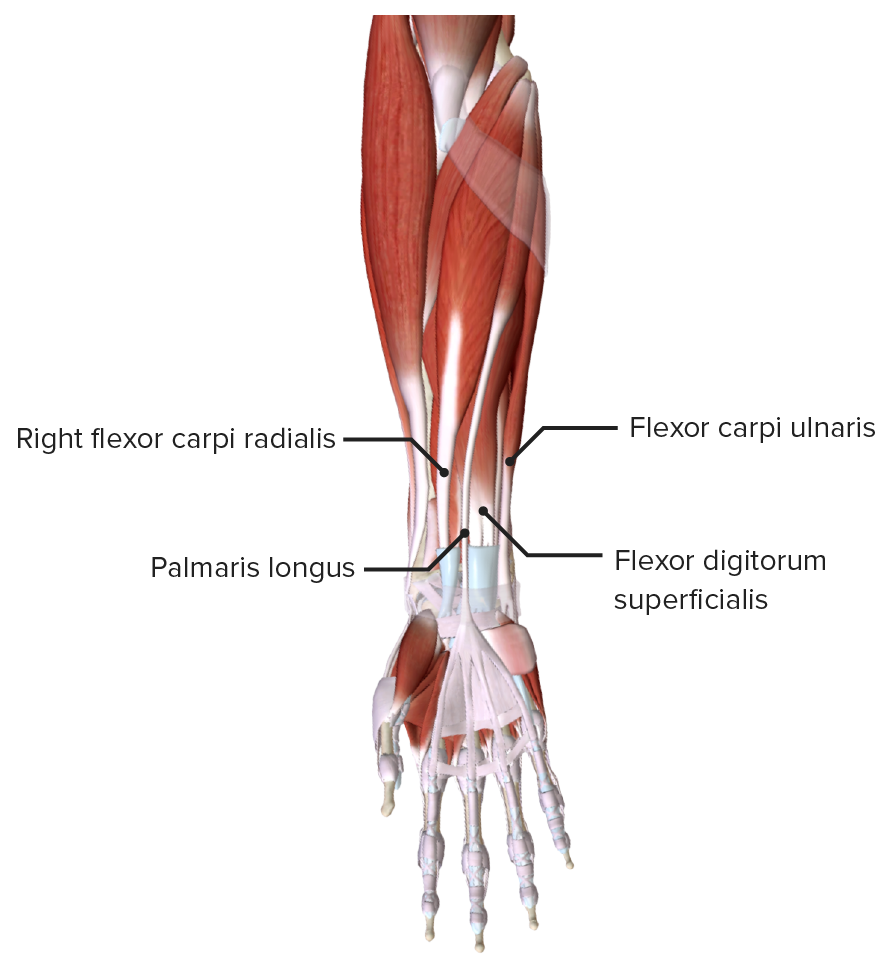
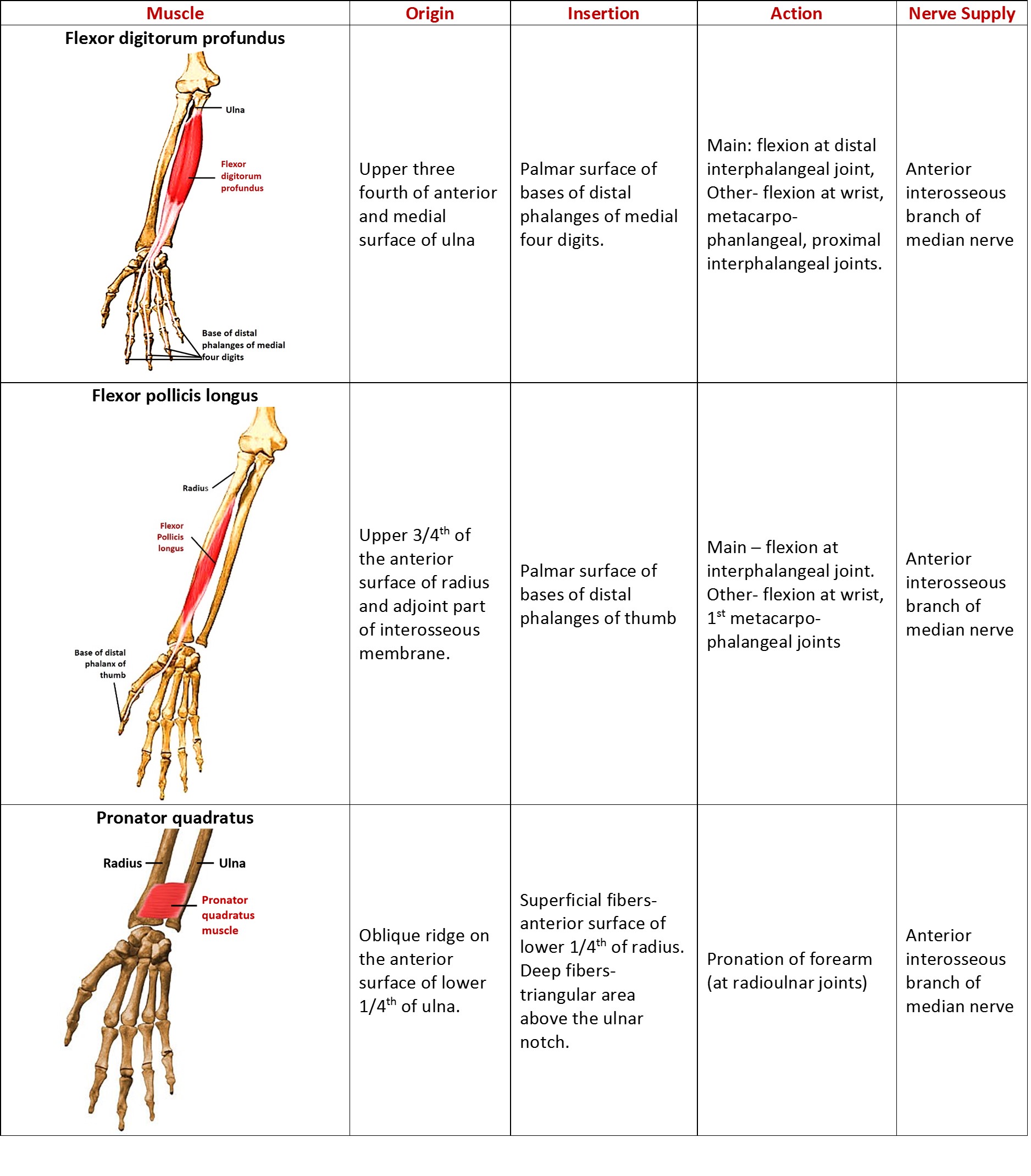
The muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm are organised into three layers:. Superficial: flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus, flexor carpi radialis, pronator teres.; Intermediate: flexor digitorum superficialis.; Deep: flexor pollicis longus, flexor digitorum profundus and pronator quadratus.; This muscle group is associated with pronation of the forearm, flexion of the wrist.

Flexor and Extensor Tendons in Fingers Anatomy Insertion of central
Chapter 48 Extensor and Flexor Tendon Injuries in the Hand, Wrist, and Foot Peter E. Sokolove and David K. Barnes Extensor Tendons Extensor tendons are quite superficial, covered only by skin and a thin layer of fascia, and are thus highly susceptible to injury by commonly experienced trauma. Such injuries may result from lacerations, bites,…
Forearm Flexor and Extensor Compartments Anatomy QA
The single-tendoned muscles, such as the extensor indicis (EI), extensor digiti minimi (EDM), and flexor pollicis longus (FPL), also activate or assist in the extension or flexion of specific fingers. When the electrode was moved to the next adjacent grid point from one point (e.g., from p1 to p2), there was partial overlap in the coverage.
Body Anatomy Upper Extremity Tendons The Hand Society
Definition. Tenosynovitis of the hand and wrist are a group of entities with a common pathology involving the extrinsic tendons of the hand and wrist and their corresponding retinacular sheaths. They usually start as tendon irritation manifesting as pain, and can progress to catching and locking when tendon gliding fails.

Flexors & Extensors of the Hand
The wrist extensor muscles comprise a significant component of the posterior forearm musculature. These muscles generally originate on or near the lateral epicondyle and insert on the distal forearm or in the hand. Clinical pathology affecting one or multiple muscles in this group is not uncommon. For example, lateral epicondylitis affects 1-5% of the general population.[1][2]